Troubleshooting
Fax Errors
What do fax error messages mean, how do I fix them?
Occasionally faxes don’t complete, usually because of some issue between the two fax systems. The fax audit log will indicate what message it failed with.
- “Call not answered or not negotiated:
The outbound call was not answered by the far end so no fax transmission could be attempted
- The call dropped prematurely:
The call dropped due to a non-fax transmission error. It is likely that the receiver hung up.
- Timed out waiting for initial communication:
A call was established with the receiver and the fax service attempted to establish a fax session, but there was no fax response from the receiver. This could be due to there being no fax machine on the receiving end, or a lack of call clarity.
- Failed to train with any of the compatible modems:
A remote fax machine was detected, but the sending and receiving modems could not establish communication.
- Fax transmission not established:
We could not detect a remote fax machine. This could be due to there being no fax machine on the receiving end, or a lack of call clarity.
- No response after sending a page:
The remote fax machine did not acknowledge that a page of the fax was received. Depending on the remote machine’s behavior, it may have still printed the page and any preceding pages.
- Received no response to DCS or TCF:
The fax service could not successfully determine the remote machine’s fax capabilities.
- The HDLC carrier did not stop in a timely manner:
The fax service initiated a fax transmission with the receiver, but there was a synchronization (timing) error that could not be resolved.
- Timed out waiting for the first message:
A call was established with the receiver and the fax service attempted to establish a fax session, but there was no fax response from the receiver. This could be due to there being no fax machine on the receiving end, or a lack of call clarity.
- Unexpected DCN while waiting for DCS or DIS:
The remote fax machine unexpectedly sent a disconnect message when the fax service asked for the remote fax machine’s fax capabilities.
- Received bad response to DCS or training:
An unexpected message was received when the fax service asked for the remote fax machine’s fax capabilities.
- Invalid response after sending a page:
An unexpected message was received after successfully sending a page. Depending on the remote machine’s behavior, it may have still printed the sent page and any preceding pages.
- Disconnected after permitted retries:
The fax service attempted to send the same message multiple times unsuccessfully. This may be due to a call clarity issue.
- Far end cannot receive at the resolution of the image:
The remote fax machine does not support receiving faxes sent at the resolution that our service sends at.
- Received a DCN from remote after sending a page:
The remote fax machine responded with a disconnect message after a page was sent successfully. Depending on the remote machine’s behavior, it may have still printed the sent page and any preceding pages.
- Unexpected message received:
The fax service received a message that it did not expect given the current context.
- Received other than DIS while waiting for DIS:
The fax service expected to receive the remote fax machine’s fax capabilities, but received an unexpected message instead.
- Unexpected DCN after EOM or MPS sequence:
The remote fax machine disconnected unexpectedly after receiving a page of a multi page fax. Depending on the remote machine’s behavior, it may have still printed the sent page and any preceding pages.
- Document loading error:
The fax service attempted to generate the message to send, but a document was missing.
- Invalid ECM response received from receiver:
The fax service received an invalid error correction message from the remote fax machine.
- Unexpected DCN after RR/RNR sequence:
The remote fax machine disconnected unexpectedly after indicating that it was not ready to initiate a fax session.
Poor WiFi Call Quality on mobile app
Call quality is primarily dependent on the local network and network conditions however there are some key concepts to keep in mind:
WiFi mode
Check on your mobile device if you are connected over 2.4Ghz or 5Ghz. Often times even if the router supports both your phone may opt into a slower, less capable connection. The 2.4Ghz spectrum is quite busy these days.
Important
If you are on a 2.4Ghz network, even if the router supports the latest Wireless N standard, if there are other wireless endpoints connecting using older B or G standards, the entire access point must slow its antenna down to the slowest device. Check your routers client list to see if there is some hidden dead weight slowing down your network
Channel Density
If your router only supports 2.4Ghz it is also likely its still on the default channel. If you are in a dense area with lots of WiFi traffic, many routers could be on the same channel leading to over-crowding in that part of the spectrum.
Using a wireless analyzer app such as Windows WiFi Analyzer or Android WiFi Analyzer will give you an idea what channels around you are in use and what are clear.
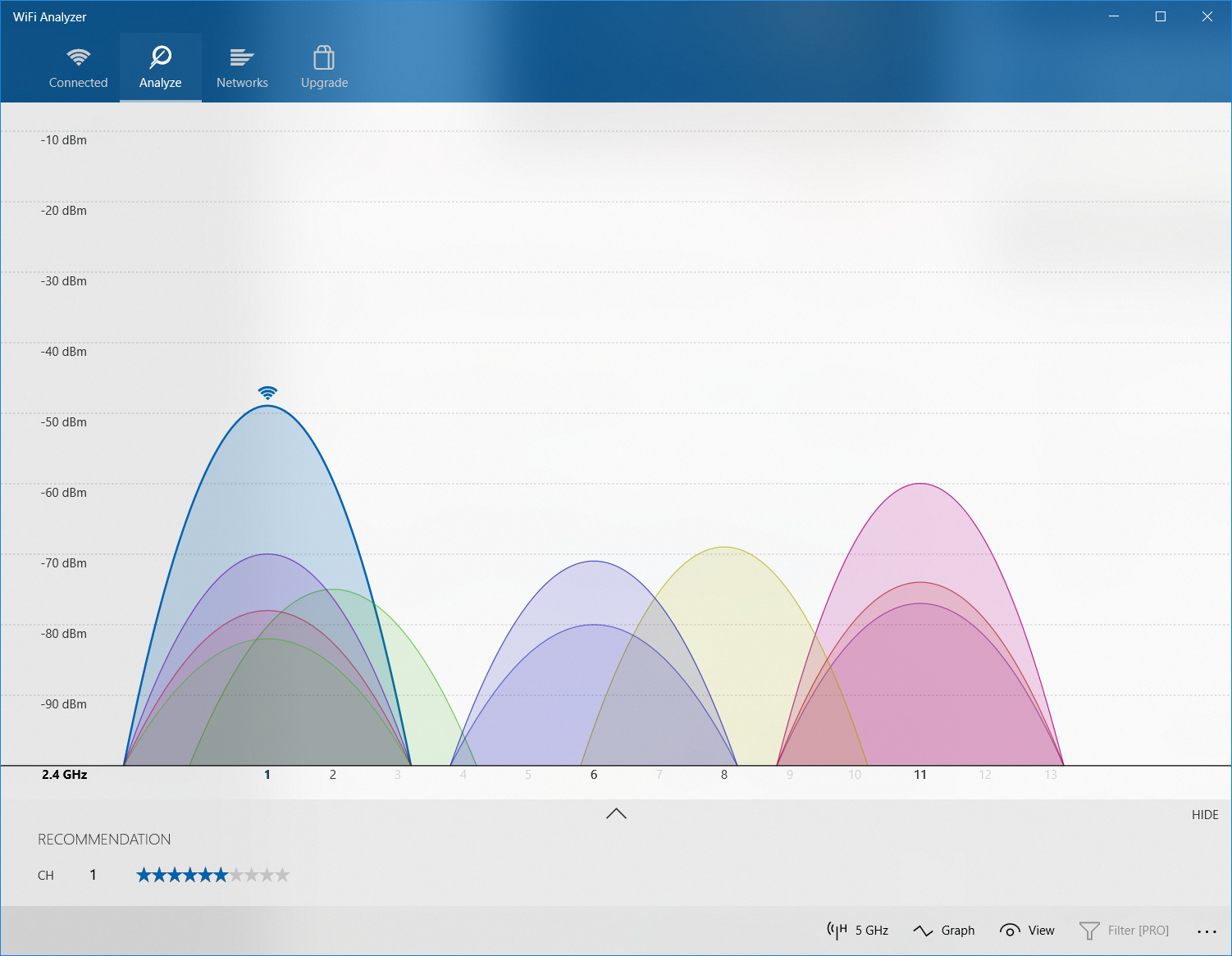
Try configuring your router to use an unused, or lesser used channel and eliminate some interference.
2.4Ghz vs 5Ghz
The primary differences between the two frequencies are the range (coverage) and bandwidth (speed) that the bands provide. The 2.4 GHz band provides coverage at a longer range but transmits data at slower speeds. The 5 GHz band provides less coverage but transmits data at faster speeds.
The range is lower in the 5 GHz band because higher frequencies cannot penetrate solid objects, such as walls and floors. However, higher frequencies allow data to be transmitted faster than lower frequencies, so the 5 GHz band allows you to upload and download files faster.
Your WiFi connection on a particular frequency band can also be faster or slower because of interference from other devices. Many WiFi-enabled technologies and other household devices use the 2.4 GHz band, including microwaves and garage door openers. When multiple devices attempt to use the same radio space, overcrowding occurs. The 5 GHz band tends to have less overcrowding than the 2.4GHz band because fewer devices use it and because it has 23 channels for devices to use, while the 2.4GHz band has only 11 channels. The number of channels that are available to you depends on the regulatory domain. If you’re experiencing a lot of interference from other devices, consider using the 5 GHz band.
Poor 4G Call Quality on mobile app
Poor mobile coverage or slow data speeds can cause call quality to suffer when using 4G data.
You can use the echo service by dialing *0000 which will just echo back anything said then open the active call info screen
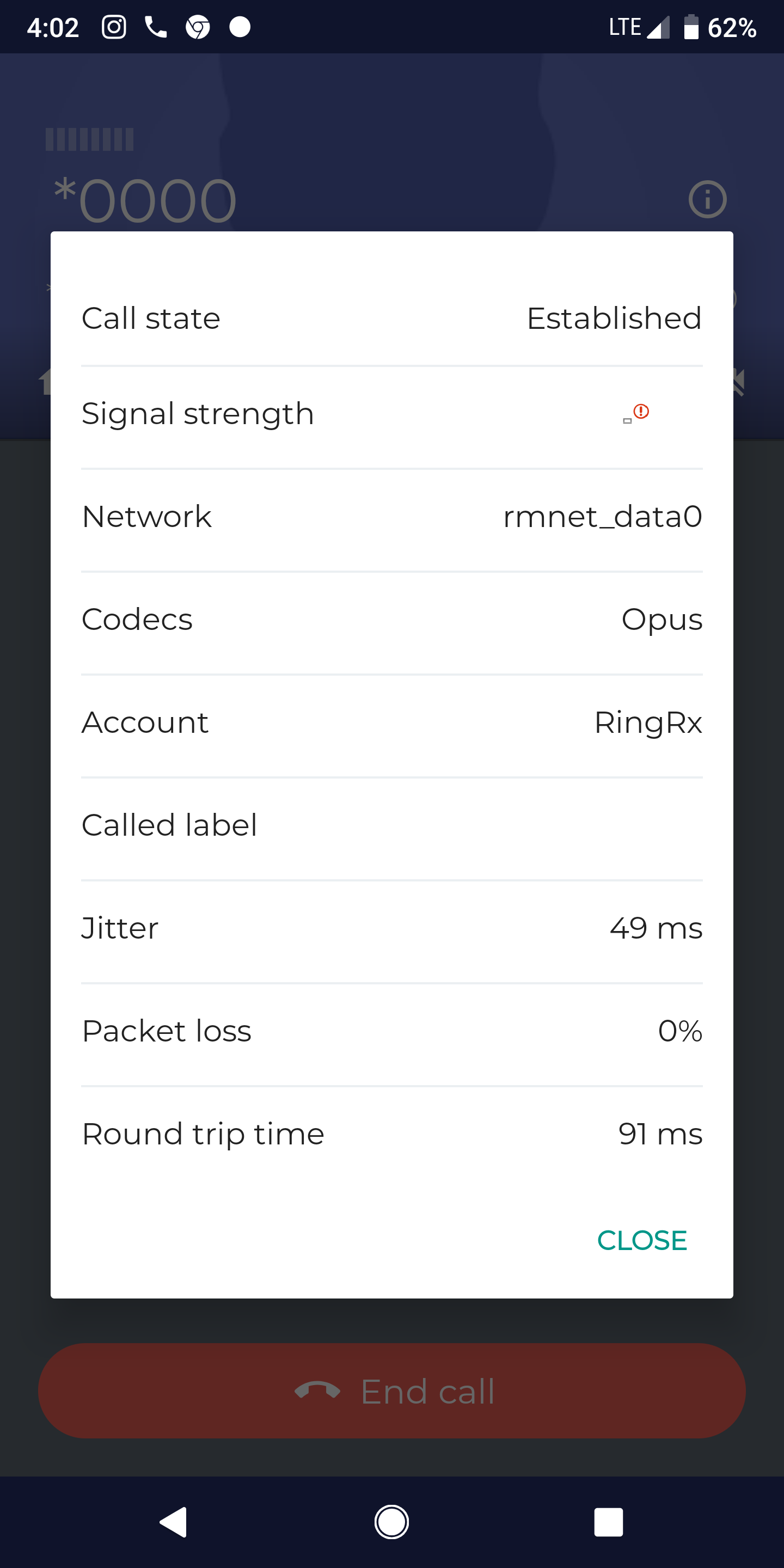
- Signal Strength:
Even with relatively poor signal strength packet loss can be low and quality high
- Jitter:
Jitter above 200ms can cause poor audio quality. Even slow network connections, if consistent can produce excellent voice quality. Jitter is a measure of consistency
- Packet Loss:
Packet loss is the ultimate enemy of voice quality. if there is a sizable amount of packet loss your connection is experiencing major issues and may be unsuitable for reliable voice communications.
- Round Trip Time:
This has little impact on quality if jitter is low. If jitter is high and round trip time is also very high (over 250ms) this may indicate severe 4G congestion or mobile provider data issues.
Note
The Opus codec uses a forward error correction algorithm to produce a high quality, full HD audio experience even with a few percent packet loss. It truly is the way of the future
Network Quality of Service
As with any other service using the internet, the connection is only as good or reliable as your internet connection. Often times that means if your internet connection is trying to do many things at once, congestion can occur which can impact the quality of your RingRx experience.
RingRx recommends using the following methods to configure your networks QoS policies for the best possible experience with the most preferred, best performing option listed first, and proceeding in order of descending preference
DSCP Tagging
RingRx has adopted easy, universal standards for tagging its traffic to allow you to setup QoS rules in your edge router to easily identify and prioritize voice traffic.
All Signaling traffic from RingRx (call control, setup etc) will be tagged as:
- DSCP:
26
- TOS:
AF31
More importantly all media traffic (the actual voice path) will be tagged as:
- DSCP:
46
- TOS:
EF
These QoS tags will remain consistent for traffic both from the RingRx network as well as cross the RingRx ecosystem (Desk phone, mobile apps etc)
QoS by Port
RingRx is an elastic cloud platform and so we encourage users to configure their networks using DSCP tagging to ensure things are always prioritized correctly, however if your router does not support this you can also configure port rules for network services as below:
Traffic |
Port Range |
Description |
|---|---|---|
UDP Traffic From or To |
16000-20000 |
This is the Media path and needs the highest or realtime priority |
TCP Traffic To port |
7770-7771 |
This is the Signaling path and needs lower priority |
TCP Traffic To port |
10443 |
This is the Signaling path for the WebRTC softphone |
We strongly recommend not to link QoS rules to specific IP’s as those may change and lead to inconsistent experience.
QoS by Network segment
Another strategy that can be used, if port or packet tagging rules are not an option is to isolate all telephony traffic to its own network space, i.e. all phones go onto a separate vlan and then you can manually enforce priority for all traffic from or to that vlan in your edge router or firewall
Important
Setting quality of service on upload will impact the consistency and quality of audio the far end party experiences. Setting quality of service on your download will impact the consistency and quality of audio you experience.
If your network equipment cannot be configured according to any of these methods, contact support and we are happy to make a recommendation or help point you in the right direction for a successful deployment